- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
How to Specify Inconel 617 Round Bars for Engineering Projects?
When choosing Inconel 617 round bars for engineering projects, it's important to think about the required operating temperature, chemical makeup standards, and allowable size differences. This nickel-chromium-cobalt-molybdenum superalloy works very well in high-temperature situations (up to 1200°C), which makes it an important material choice for parts of aircraft turbines, equipment used in petrochemical processing, and power generation systems. Understanding the standards, such as ASTM B166 compliance, surface finish needs, and mechanical properties, is important for getting the best performance in tough industrial settings where material failure is not an option.
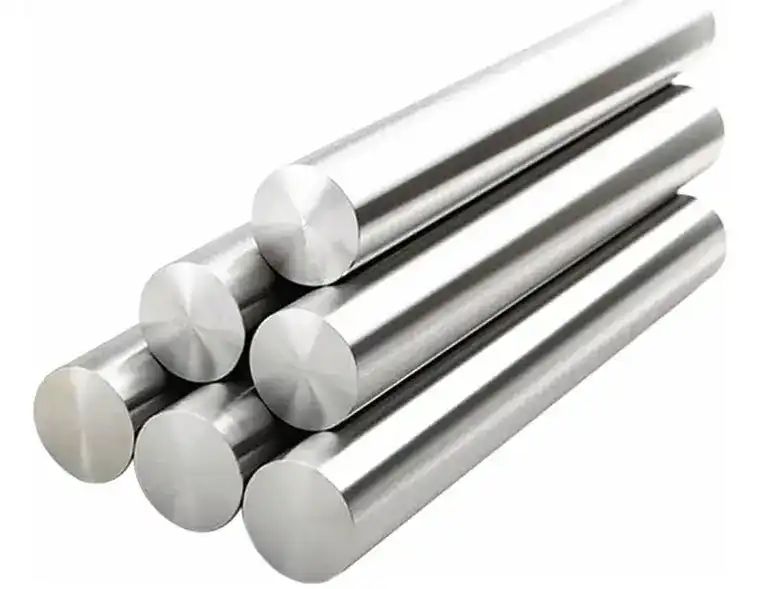

Understanding Inconel 617 Round Bars
For high-temperature engineering uses, Inconel 617 round bars are one of the most modern nickel-based superalloys that can be found. This amazing material has great resistance to oxidation and immense mechanical strength, which makes it essential in many industry fields. Nickel makes up 44-52% of the alloy's unique chemical makeup. It is joined by chromium (20–23%), cobalt (12–15%), and molybdenum (8–10%), which together form a mechanical structure that stays strong under high temperatures.
Chemical Composition and Material Properties
Because the chemicals in Inconel 617 are perfectly balanced, it has better performance qualities than regular stainless steels and other nickel alloys. Chromium protects against rust, and cobalt makes things stronger at high temperatures and less likely to break down due to heat. Molybdenum helps make solid solutions stronger and makes them more resistant to surroundings that are reducing. This carefully designed mixture has a minimum tensile strength of 760 MPa, a minimum yield strength of 350 MPa, and amazing elongation qualities of 30% minimum, making it reliable in important situations.
Industry Standards and Certifications
When specifying these materials, engineering teams must make sure they meet set industry standards as a top priority. ASTM B166, ASME SB166, and EN 10095 are the main standards that control the production of Inconel 617 round bars. These rules say what kinds of chemicals can be used, how strong they should be, how accurate the measurements must be, and how they must be tested. Quality control at the aerospace level is guaranteed by AS9100D certification, and material test certificates (MTC) and SGS test reports provide traceable paperwork that is needed for project audits and regulatory compliance.
Available Dimensions and Customization Options
Standard diameter sizes are usually between 5 mm and 300 mm, and lengths can be anywhere from 3000 mm to 6000 mm to meet most engineering needs. For specific uses, advanced production techniques allow for custom sizes up to 500 mm in diameter. Surface treatments like anodizing and sanding make things less likely to rust and improve the quality of the finish on the surface. Engineers can choose the finish they need based on the needs of the product and how the part will be machined because surfaces can be peeled, turned, ground, or polished.
Critical Considerations When Specifying Inconel 617 Round Bars
To properly specify a material, you need to look at all of the operational factors and environmental conditions that can affect how well the material works. Temperature exposure is the most important thing to think about because Inconel 617 can withstand extended temperatures of up to 1200°C and doesn't get damaged by thermal shock or cycling fatigue. Evaluating the risk of corrosion is also very important, especially in naval settings, chemical processing plants, and offshore uses where chloride stress corrosion cracking is a big problem.
Temperature and Environmental Requirements
Operating temperature profiles have a big effect on the choices of materials and the long-term performance standards. Inconel 617 has a 15% higher creep strength than normal grades thanks to advanced thermomechanical processing that makes it very resistant to creep at high temperatures. The alloy doesn't oxidize easily at temperatures above 1000°C, which makes it a good choice for gas engine parts and combustion chamber uses. Performance stays stable in cold temperatures down to -60°C, which makes it reliable for Arctic offshore sites and high-altitude aerospace uses.
Machining and Fabrication Considerations
Because Inconel 617 is hard to machine, you need to use special methods and tools to get the best results while keeping the material's structure. To keep surfaces from getting damaged and measurements from being off, work hardening requires steady feed rates and sharp cutting tools. The right machining factors include the right choice of coolant, cutting speed, and feed rate to keep heat buildup and tool wear to a minimum. Specifications for surface finish must take into account the next steps in the process and the needs of the end application. Following AMS 2701 guidelines will ensure surfaces that are good enough for aerospace use.
Comparative Analysis with Alternative Materials
Comparing different superalloys and high-performance materials in a planned way can help with material selection. Inconel 625 is more resistant to rust but can't handle higher temperatures. Inconel 718 is stronger but less resistant to oxidation above 650°C. Alternatives to 316L or 17-4 PH stainless steel are cheaper, but they don't work well at high temperatures. Titanium metals have great strength-to-weight ratios, but they don't hold up well to high temperatures and cost more to make. This framework for comparison lets you make smart choices based on performance needs, price limits, and application-specific needs.
Procurement Guide for Inconel 617 Round Bars
To make sure a project is a success, the world supply chain for specialized superalloys needs to be planned out and suppliers evaluated. Inconel 617 round bars are hard to get, expensive, and take a long time to get because of changes in the market. The prices of nickel, chromium, and cobalt affect the costs of raw materials, and when demand is high, production capacity issues can make delivery times longer. Knowing about these market factors helps with making purchases and keeping track of budgets.
Supplier Evaluation and Quality Assurance
To choose reliable providers, you need to carefully check their manufacturing skills, quality control systems, and compliance with certifications. AS9100D certification means that the quality management system meets aerospace standards, while ISO 9001 certification means that the basic quality strategy is being used. Audits of manufacturing facilities should check the accuracy of CNC machines, checking tools, and systems for tracking materials. Using optical emission spectrometry (OES) for chemical analysis, mechanical testing tools for hardness and tensile testing, and ASTM G28 testing for corrosion proof to make sure the quality is complete.
An review of a supplier's track record includes metrics for delivery performance, customer references, and the ability to provide technical support. For big orders, a reliable supplier should keep 98% of deliveries on time and offer technical support throughout the buying process. Laser-marked material test records with heat and charge numbers are required for material certification. This allows full traceability from where the raw materials come from to where they are delivered.
Lead Times and Inventory Management
Standard wait times for Inconel 617 round bars are between 6 and 12 weeks for custom orders. Items that are already certified may ship within 2 to 3 weeks. Large orders of more than 50 tons often have longer wait times of 16 to 20 weeks because of the time it takes to get the raw materials and schedule production. When planning strategically for inventory, these longer wait times should be taken into account, along with the need to balance carrying costs and project timelines.
Buying in bulk can help you save money and make sure that materials are always available for projects that have more than one part. Minimum order numbers vary by supplier and specification, but for standard grades, they are usually between 500 kg and 2 tons. When you buy more than 10 tons, you can often get big discounts on the price. This makes consolidated buying a good idea for big projects or yearly supply agreements.
Practical Case Studies and Industry Applications
Real-world performance data shows that Inconel 617 round bars are very useful in a wide range of challenging industrial settings. These case studies show how choosing the right materials and suppliers can help a project succeed. They also show common problems and good ways to fix them.
Aerospace Combustion Chamber Components
A major aircraft company successfully used Inconel 617 round bars to make combustion liners for next-generation turbine engines. For the job, it had to keep running at 1150°C for a long time, and the temperature had to change quickly when the engine started up and shut down. One of the first problems with specifying the material was getting the dimensions to within 0.05 mm while still meeting the standards for the surface finish needed for the best combustion efficiency.
As an answer, engineers worked together with material suppliers to find the best heat treatment parameters and machining sequences. Advanced thermomechanical processing made the creep rupture strength 15% higher than in normal grades. This added 2,000 hours of service life to the part. A third party confirmed that the material had better thermal fatigue resistance, which allowed for confident approval for use in hypersonic vehicles.
Offshore Oil Platform Heat Exchangers
For an offshore drilling job, heat exchanger tubes had to be able to handle high temperatures and H2S environments without cracking from chloride stress corrosion. Pitting corrosion and stress cracking caused traditional stainless steel choices to break after 18 months. The base for making custom tubes out of Inconel 617 round bars gave them better corrosion protection and mechanical strength.
As part of the application process, a lot of tests were done on the materials according to ASTM G28 standards for acidic environments. These tests showed that the materials were very resistant to stress corrosion cracking. Arctic-grade approval made it possible to work reliably at -60°C during winter shutdowns. The installation lasted 5 years with little upkeep, showing that it was more cost-effective than other products.
Power Generation Turbine Blades
A project to update a nuclear power plant needed materials for the turbine blades that could be used for longer periods of time at 980°C and had better shift resistance. For the application, strict material tracking and nuclear-grade quality assurance rules were needed. These strict standards were met by Inconel 617 round bars, which also had better mechanical properties than other blade materials.
One of the hardest parts of manufacturing was making blades with complicated shapes while keeping the material's qualities stable during the whole process. Cutting parameters and heat treatment steps were made better by material suppliers and machining experts working together closely. The new parts had 25% longer service intervals than the old blade materials, which cut down on repair costs and increased plant availability.
Conclusion
For engineering projects, choosing Inconel 617 round bars requires a deep knowledge of the material's properties, the needs of the application, and the supplier's abilities. To be successful, you need to carefully look at the weather exposure, corrosion environment, and mechanical loading conditions, and make sure that you follow all industry standards. To help projects stay on schedule and within budget, good buying strategies stress the importance of qualified suppliers, quality control procedures, and smart inventory management. The written case studies show that the materials work well in aerospace, offshore, and power generation settings. This proves that proper material selection and working together with a seller are important for meeting project goals.
FAQ
1.What diameter ranges are available for Inconel 617 round bars?
Standard diameter ranges span from 5mm to 300mm with length options between 3000-6000mm. Custom dimensions up to 500mm diameter are available for specialized applications requiring non-standard sizing.
2.Which industry standards apply to Inconel 617 round bars?
Primary standards include ASTM B166, ASME SB166, and EN 10095 for chemical composition and mechanical properties. AS9100D certification ensures aerospace-grade quality management, while AMS 2701 governs surface finish requirements.
3.What surface treatments are available for these materials?
Available surface treatments include sandblasting and anodizing for enhanced corrosion resistance. Standard surface finishes encompass peeled/turned, ground, or polished options to meet specific application requirements.
4.How should I evaluate suppliers for Inconel 617 round bars?
Evaluate suppliers based on AS9100D certification, manufacturing capabilities including CNC precision equipment, and quality assurance protocols. Verify chemical analysis capabilities, material traceability systems, and delivery performance metrics for large volume orders.
5.What are typical lead times for custom specifications?
Standard lead times range from 6-12 weeks for custom specifications, while pre-certified stock items may ship within 2-3 weeks. Large volume orders exceeding 50 tons typically require 16-20 weeks due to manufacturing capacity scheduling.
6.What documentation is provided with material certification?
Complete material certification includes MTC (Material Test Certificates) and SGS test reports with full chemical analysis, mechanical properties testing, and dimensional verification. Laser-marked heat and charge numbers ensure complete traceability throughout the supply chain.
Partner with TSM Technology for Premium Inconel 617 Round Bar Solutions
For important engineering uses, TSM Technology provides Inconel 617 round bars that are precisely designed and go above and beyond industry standards. Our AS9100D-certified factories use cutting-edge CNC technology on 8 production lines and more than 100 tools to make sure that the sizes of the parts we make meet the needs of the aerospace and energy sectors. We have 14 years of experience working with nickel-based superalloys and can help you with everything from choosing the right materials to delivering them. Get in touch with our engineering team at info@tsmnialloy.com to talk about your project needs and find out why top manufacturers trust TSM Technology as their Inconel 617 round bar provider.
References
Davis, J.R., ed. "ASM Specialty Handbook: Heat-Resistant Materials." ASM International, Materials Park, Ohio, 1997.
Donachie, Matthew J. and Stephen J. Donachie. "Superalloys: A Technical Guide, Second Edition." ASM International, 2002.
Reed, Roger C. "The Superalloys: Fundamentals and Applications." Cambridge University Press, 2006.
Campbell, Flake C. "Manufacturing Technology for Aerospace Structural Materials." Elsevier Science & Technology, 2006.
Sims, Chester T., Norman S. Stoloff, and William C. Hagel, eds. "Superalloys II: High-Temperature Materials for Aerospace and Industrial Power." John Wiley & Sons, 1987.
Tien, John K. and Thomas Caulfield, eds. "Superalloys, Supercomposites and Superceramics." Academic Press Professional, 1989.
Learn about our latest products and discounts through SMS or email