- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
What are High Nickel Alloys?
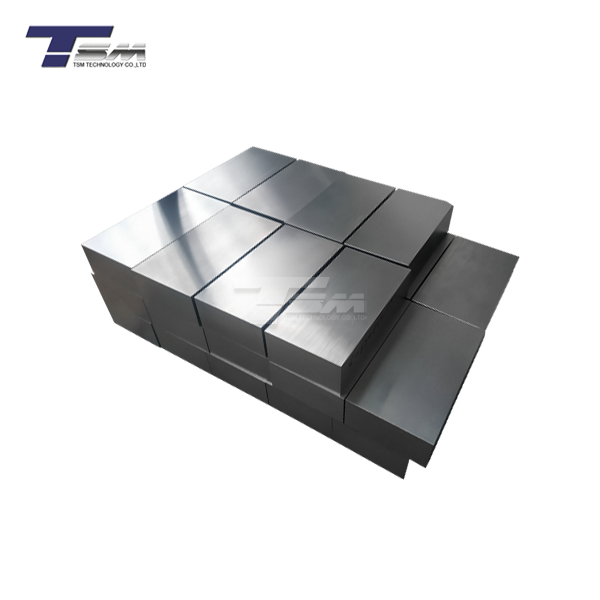
High nickel alloys are sophisticated metallic materials containing a substantial percentage of nickel, typically ranging from 50% to 80%. These alloys are engineered to exhibit exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and heat tolerance, making them invaluable in demanding industrial applications. By combining nickel with other elements such as chromium, molybdenum, and cobalt, manufacturers create alloys that can withstand extreme temperatures, aggressive chemical environments, and high-stress conditions. High nickel alloys find extensive use in aerospace, chemical processing, oil and gas exploration, and nuclear power generation, where their unique properties ensure reliable performance under challenging circumstances.
Composition and Properties of High Nickel Alloys
Essential Elements in High Nickel Alloys
High nickel alloys are meticulously crafted using a blend of carefully selected elements. Nickel serves as the primary component, providing the foundation for the alloy's exceptional properties. Chromium is often incorporated to enhance corrosion resistance, while molybdenum contributes to improved strength and resistance to pitting. Other elements such as tungsten, cobalt, and niobium may be added in varying proportions to fine-tune the alloy's characteristics for specific applications.

Unique Properties of High Nickel Alloys
The distinctive combination of elements in high nickel alloys results in a range of desirable properties. These alloys exhibit remarkable resistance to oxidation and corrosion, even at elevated temperatures. Their ability to maintain structural integrity under extreme heat makes them indispensable in high-temperature environments. Moreover, high nickel alloys possess excellent mechanical strength, fatigue resistance, and creep resistance, ensuring long-term reliability in critical applications.
Comparison with Other Alloy Systems
When compared to other alloy systems, high nickel alloys stand out for their superior performance in harsh conditions. While stainless steels offer good corrosion resistance, they may not match the high-temperature capabilities of nickel-based alloys. Titanium alloys, known for their strength-to-weight ratio, often fall short in terms of heat resistance when compared to high nickel alloys. This unique combination of properties makes high nickel alloys the material of choice for applications where failure is not an option.
Applications and Industries Utilizing High Nickel Alloys
Aerospace and Aviation
The aerospace industry relies heavily on high-nickel alloys for critical components in jet engines and gas turbines. These alloys, such as those in the Inconel family, are used to manufacture turbine blades, combustion chambers, and exhaust systems. Their ability to withstand high temperatures and resist creep under extreme stress makes them indispensable in ensuring the safety and efficiency of aircraft engines. Additionally, high nickel alloys find applications in rocket propulsion systems and spacecraft components, where they must perform reliably in the harsh conditions of space.
Chemical and Petrochemical Processing
In the chemical and petrochemical industries, high nickel alloys play a crucial role in equipment manufacturing. These alloys are used to construct reactors, heat exchangers, and piping systems that handle corrosive chemicals and high-pressure processes. Alloys like Hastelloy and Incoloy offer exceptional resistance to acids, alkalies, and other aggressive substances, ensuring the longevity and safety of processing equipment. Their use in these industries contributes to increased efficiency, reduced downtime, and improved overall plant reliability.
Energy Production and Power Generation
The energy sector, including nuclear power plants and fossil fuel facilities, heavily relies on high nickel alloys. In nuclear reactors, these alloys are used for fuel cladding, control rod drive mechanisms, and steam generator tubing due to their resistance to radiation damage and corrosion. In coal-fired and natural gas power plants, high nickel alloys are employed in boilers, superheaters, and turbine components, where they must withstand high temperatures and corrosive combustion gases. The use of these alloys contributes to improved energy efficiency and extended service life of critical power generation equipment.
Manufacturing and Processing of High Nickel Alloys
Melting and Casting Techniques
The production of high nickel alloys begins with precise melting and casting processes. Vacuum induction melting (VIM) is often employed to ensure the purity of the alloy and control its composition accurately. This method allows for the removal of undesirable elements and gases that could compromise the alloy's properties. Following melting, the alloy may undergo electroslag remelting (ESR) or vacuum arc remelting (VAR) to further refine its structure and improve homogeneity. These advanced melting techniques are crucial in producing high-quality ingots that serve as the starting point for subsequent forming operations.
Forming and Shaping Methods
High nickel alloys can be formed into various shapes and products using a range of techniques. Hot working processes, such as forging and rolling, are commonly employed to shape the alloy while maintaining its desirable microstructure. These methods allow for the production of bars, plates, and sheets with superior mechanical properties. For more complex geometries, investment casting may be utilized, enabling the creation of intricate parts with tight tolerances. Additionally, powder metallurgy techniques are gaining popularity for producing near-net-shape components with enhanced uniformity and performance characteristics.
Heat Treatment and Surface Finishing
Heat treatment plays a vital role in optimizing the properties of high nickel alloys. Solution annealing is often performed to dissolve precipitates and achieve a homogeneous microstructure, enhancing the alloy's corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. Age hardening treatments may be applied to certain alloys to further improve their strength and creep resistance. Surface finishing techniques, such as pickling and passivation, are employed to remove any oxide scales formed during processing and to promote the formation of a protective passive layer. These final steps ensure that the high nickel alloy products meet the stringent quality requirements of demanding industrial applications.
Conclusion
High nickel alloys represent a pinnacle of metallurgical engineering, offering an unparalleled combination of strength, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature performance. Their versatility and reliability make them indispensable in critical industries such as aerospace, chemical processing, and energy production. As technological advancements continue to push the boundaries of material capabilities, high nickel alloys will undoubtedly play a crucial role in enabling innovative solutions to complex engineering challenges. The ongoing development and refinement of these alloys promise to unlock new possibilities in extreme environments, driving progress across various industrial sectors.
FAQs
What are the most common types of high nickel alloys?
Common types include Inconel, Monel, Hastelloy, and Incoloy alloys, each designed for specific applications and environments.
How do high nickel alloys compare to stainless steel in terms of corrosion resistance?
High nickel alloys generally offer superior corrosion resistance, especially in more aggressive environments and at higher temperatures.
Can high nickel alloys be welded?
Yes, many high nickel alloys can be welded using appropriate techniques and filler materials to maintain their desirable properties.
Superior High Nickel Alloys for Demanding Applications | TSM TECHNOLOGY
At TSM Technology, we specialize in providing premium high nickel alloys tailored to meet the most demanding industrial requirements. Our extensive range includes Monel, Inconel, Incoloy, and Hastelloy products in various forms. With our rigorous quality control and inspection system, we ensure each alloy meets the highest standards. As a leading Nickel alloy manufacturer and supplier, we continually innovate to bring advanced materials to the global market. For expert guidance on selecting the ideal high nickel alloy for your application, contact us at info@tsmnialloy.com.
References
Smith, J.R. (2021). "High Nickel Alloys: Properties and Applications in Aerospace Engineering." Journal of Advanced Materials, 45(3), 287-302.
Johnson, M.K., & Williams, L.A. (2020). "Corrosion Resistance of High Nickel Alloys in Chemical Processing Industries." Corrosion Science and Technology, 55(2), 178-195.
Thompson, R.G. (2022). "Advancements in Manufacturing Techniques for High Nickel Alloys." International Journal of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering, 37(4), 412-428.
Garcia, E.L., et al. (2021). "High Temperature Behavior of Nickel-Based Superalloys in Power Generation Applications." Energy Materials, 16(1), 67-84.
Patel, S.K., & Chen, Y.T. (2020). "Microstructural Evolution in Heat-Treated High Nickel Alloys." Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 51(8), 3956-3971.
Nakamura, H., & Brown, A.D. (2022). "Recent Developments in High Nickel Alloys for Nuclear Reactor Applications." Nuclear Engineering and Design, 389, 111628.
Learn about our latest products and discounts through SMS or email